 Abengoa
Abengoa
Annual Report 2009
- Corporate Social Responsibility Report
- Commitment to Innovation
- Innovative Solutions for Sustainability
Innovation is the vehicle through which Abengoa develops innovative solutions for sustainability, and the key driver of the global evolution towards a sustainable world boasting high standards of well-being for peoples and nations.
A commitment to innovation means a commitment to sustainability. R&D investment ensures that technological development is the cornerstone of Abengoa’s sustainable growth, as well as the basis for meeting the company’s chief strategic objectives. R&D management takes into account the characteristics of business R&D, which is focused on results and aligned with strategy.
Innovation, geared towards obtaining results, pursues three types of tangible goals: diversification, achieved by developing new products and services; differentiation, attained by perfecting and adapting existing products and services to new demands; and process improvement. Abengoa also pursues the intangible aim of acquiring essential competencies and, above all, generating future options, an aspect that is closely linked to value through expectations of growth and new business development.
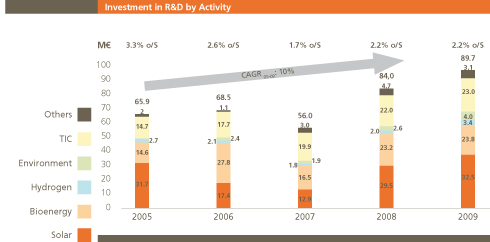
Abengoa’s R&D investment in 2009 totaled 89.7M€, up 7% from last year, thus representing approximately 2.2% of company sales and an upward trend of 8% annual growth of said investment.
The table below shows Abengoa’s R&D investment evolution over the past five years by sector.
The process of innovation is dynamic in responding to a society in constant evolution and, therefore, the whole process is conducted utilizing all of the resources available to the society of knowledge, science and technology. As a major company, Abengoa has adopted the so-called “innovation ecosystem” and is fostering collaboration with universities, governmental agencies, public research institutions, technology centers, and other companies in pursuing the creation of networks of knowledge with Abengoa itself serving as the propelling force. This is the only way it may be in the condition to generate the required know-how and to provide the answers and solutions to the new challenges. This innovation system includes demonstration projects, research and development facilities in various countries, and external collaboration agreements. With this in mind, Abengoa signed two collaboration framework agreements in 2009 with the University of Seville, one for joint training of PhD holders, and the other for promoting collaboration between the university and Abengoa itself.
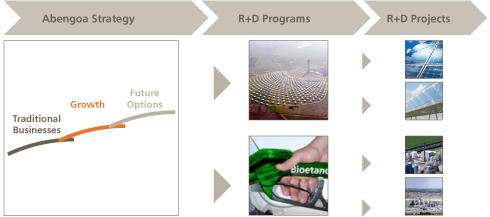
Innovation management at Abengoa is framed within company or Business Unit (BU) strategy, formalized in its three horizons, where one or more R&D Programs geared towards developing new, or innovating existing, products or processes, are defined. R&D Programs are general in nature and linked to a particular line of development.
R&D Programs are long-term (up to 30 years) propositions, and are carried out through partial programs (10 years) and specific projects (3 to 4 years). It is in these R&D&i projects in which Abengoa executes its R&D&i.
At Abengoa most R&D investment involves applied research and development of technological innovation in the company’s approach to fulfilling the strategic objectives of sustainability and creating new products.
Sustainability. Abengoa’s Business Metric
Abengoa’s efforts involving innovation and technological development are intended to serve sustainability in its three essential dimensions: social, environmental, and economic.
Abengoa’s investments in innovation bear a thoroughly positive economic and social impact by helping the local communities within which such investments are made to grow and prosper, acting as an effective and necessary instrument in the evolution towards a sustainable society that protects the environment. Innovation is not an end in itself, as sometimes occurs in the case of research, but rather embraces the mission of gearing the society towards a better world. It seeks to improve our present socioeconomic system, which is neither sustainable nor does it serve everyone, towards a more sustainable model intended for everyone. Innovation, therefore, is our commitment to the future.
Abengoa enjoys a position of international leadership in a significant number of key areas in the so-called Green Economy. Here, together with all of its business units, Abengoa has embraced a firm commitment, through innovation policy and strategy, to pursue sustainable use of resources and raw material that spans its entire lifecycle. Each Abengoa business unit engages in the various processes of technological innovation with this aim in mind.
Abengoa focuses its efforts on technological innovation in the field of energy production using renewable sources. Promotion and implementation of these technologies for producing energy are based on renewable sources featuring low environmental impact and high energy efficiency. This technological development means a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, as well as decentralization of sources as regards the conventional, in the sense of liberating nations from the usual geopolitical subordination imposed on them by those in possession of said conventional sources of energy, which are linked to today’s causes of supply insecurity and scarcity.
Below are the key areas of sustainable development in which Abengoa exerts its leadership:
- Renewable Energies
Abengoa Solar is engaged in working on electrical power production aimed at replacing conventional sources with thermoelectric and photovoltaic solar solutions, as well as at developing technologies that may enable energy storage.
In the area of Concentrating Solar Power (CSP), Abengoa is the proud owner of the world’s only two existing commercial power towers, and is developing several parabolic trough collector plants, among which is the world’s largest, located in the U.S. state of Arizona. Abengoa is clearly the world’s leading player in this field. It must be emphasized that cooperation from the solar platform in Almería has been a key factor in gaining this position of leadership, as well as the more general collaboration from the entire Center for Energy, Environmental and Technological Research (CIEMAT) in Spain.
Abengoa Bioenergy is involved in the production of first- and second-generation biofuels as replacement of traditional fossil fuels. Furthermore, focused on the use of biomass as an energy source, R&D projects are carried out with a view and readiness for their conversion to industrial projects in biomass gasification plants and hybrid biomass and CSP plants.
- Environmental Services
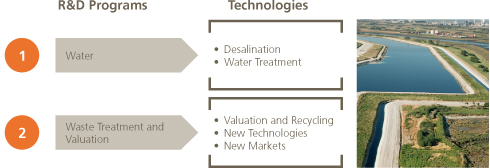
Befesa, la sociedad cabecera del grupo de negocio Servicios Medioambientales, aporta soluciones al ciclo integral del agua y a la gestión integral de residuos industriales. Genera nuevas plantas de desalación y tratamiento para el agua, así como procesos industriales de valorización de residuos.
- Information Technologies
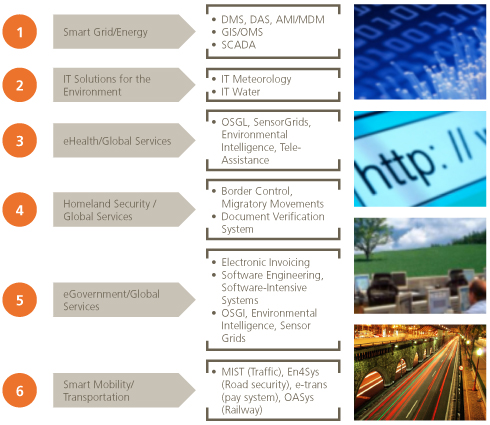
Telvent, the parent company of the IT business unit, develops smart grids that help to optimize energy consumption and grid manageability.
Smart grid is developed through R&D projects that give rise to products implemented in various parts of the world, with Telvent’s efficient smart electrical power distribution grids proving to be key players in the industry.
Telvent is also engaged in developing highly-competitive sustainable agriculture with significant contribution from new technologies: providing technological service to the U.S. agricultural complex, the largest in the world.
- Industrial Engineering and Construction
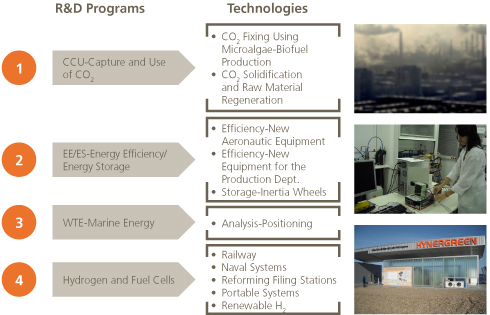
Hynergreen, a company of the Industrial Engineering and Construction business unit, develops new systems for producing hydrogen from renewable sources, in addition to the use of hydrogen in state-of-the-art fuel cells. And Inabensa is working on the implementation of energy efficiency enhancements and CO2capture and storage programs.

Case Study
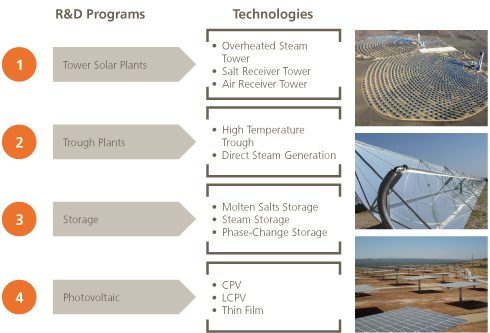
Abengoa Solar: Central Receiver and Tower Technology
The development of central receiver and tower technology has become the main element that places Abengoa Solar at the helm of its competitors in the industry. The commitment to power towers and heliostats in the company’s goal of the pursuit of higher efficiencies, particularly in the solar component of the plant, is recognized worldwide as being a distinctive Abengoa Solar quality.
In 2009, in addition to the commissioning of the Eureka plant for producing superheated steam, R&D&i projects were executed with a focus on the receiver, one of the key components of these types of plants.
The aim of the Eureka project is to address the new challenges in tower technology which, following the commissioning of the PS20, has undoubtedly and unquestionably proven its reliability. Thus, this second-generation solar power tower has managed to reach higher temperatures to produce superheated steam, thereby enhancing the global efficiency of the steam cycle. The plant is made up of 35 heliostats and a 50-m-high tower which houses the experimental superheating receiver. Plant power output capacity totals approximately 2 MW.

Parallel with the prototype manufacturing and the construction of the plant, the Resolve project, in collaboration with prestigious Spanish research centers, developed software that simulates thermo-fluid-dynamic performance in both saturated steam and superheated steam solar receivers. These efforts will continue in the Cenit Consolida project for three more years, during which time, using the experimental data being compiled, the software implemented will be validated and improved.
R&D efforts in tower technology are not only focused on steam technology: two new projects that began in 2009 have focused their attention on two very different fluids: molten salts and air.
The CRS salt project (co-financed by the Center for Industrial Technological Development) is engaged in engineering and manufacturing a solar tower receiver prototype in which the heat-bearing fluid is a blend of molten salts, the aim of which is to study the technical and economic viability on a larger scale for a plant employing this technology. The Solugás Project (co-financed by 7ºPM), which began in 2008, seeks to show how towers function at a higher temperature, using air as the heat-bearing fluid, and gas cycle instead of steam.
Case Study
Abengoa Bioenergy: Second-Generation Bioethanol
The culmination of the development of second-generation biofuels will enable society to maintain present standards of living, while protecting the environment and promoting a green economy at the same time.
Second-generation bioethanol seeks to compete with fossil fuels at a global level, once the latter’s GHG emission costs are taken into account. However, in order to reach this goal, certain challenges must be met at the technological, legislative, social and environmental levels.
Abengoa Bioenergy is also engaged in developing various other technologies, such as the processes of enzymatic hydrolysis, gasification and catalysis so that, depending on the geography and the specific features of the raw material used, bioethanol production can be optimized. In this field, Abengoa Bioenergy New Technologies (ABNT) is working on several prestigious projects, including the Hybrid Project in the U.S., and the European Bioref-integ project.
ABNT is also working on the development of new less consumption-intensive crops with higher resistance to pests and weather threats. In this area, noteworthy are the SOST-CO2 projects (with participation from Inabensa as well) which, among other objectives, seeks to design and both technically and economically evaluate the process of CO2 capture through the production of microalgae which may subsequently be used in bio-refineries, as well as the Singular Strategic Project (SSP) in energy crops.
The future of the industry will be determined not only by production evolution, but also in the generation and diffusion of knowledge for using bioethanol as a fuel. ABNT is aware of this and invests a significant amount of resources to this end, heading up projects like I+DEA that seek to meet this objective.
Innovation at Abengoa in 2009
Most of Abengoa’s R&D&i investments go into applied research and developing technological innovations in the pursuit of strategic objectives of sustainability and in generating new products. In 2009 Abengoa added a powerful tool to the R&D&i management. Based on Stage-Gate methodology, this tool serves to ensure the management of R&D Projects within a common framework of excellence, as well as project alignment with strategic objectives. This methodology outlines the main initiatives taken when preparing and developing an R&D-categorized project within the project portfolio of the Abengua BUs. The aim is to obtain the most standardized focus possible for R&D Projects through the utilization of a common methodology to define processes, maximize the value the R&D Projects add to Abengoa businesses, and minimize the risks involved.
The following show the main programs carried out in the area of innovation in 2009 by the different business units:
2009 Milestones
Abengoa Solar
Abengoa Bioenergy

Environmental Services
Information Technologies
Industrial Engineering and Construction
Abengoa’s R&D investment in 2009 totaled 89.7M€, up 7% from last year, thus representing an upward trend of 8% annual growth of said investment