 Abengoa
Abengoa
Annual Report 2009
- Corporate Social Responsibility Report
- Commitment to Corporate Social Responsability
- Our CSR Policy and Strategy
Businesses today play a crucial role in sustainability by employing their resources in ingenuity, creativity and talent to resolve some of the most pressing social and environmental issues facing humanity, and by making sure that the impact generated by their activity has a positive impact on society and the environment, achieved through ethical and transparent conduct that contributes to sustainability and the well-being of the community. It is essential that this conduct takes into account the expectations of stakeholders, abides by the law, is consistent with international standards of conduct and is integrated throughout the entire organization and put into practice in company relationships with other organizations. This conduct is what is commonly referred to as Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), corporate responsibility, or business responsibility.

Photo taken by Carlos Bustos, from Abengoa Chile, for the 1st Edition of the Abengoa Sustainability Photography Contest
In recent years, CSR has become increasingly more relevant among businesses and their stakeholders, to the point of becoming one of the aspects with the greatest bearing on an organization’s performance. More than ever, business performance in the realms of society and the environment has become, in addition to financial performance, a key factor in measuring future performance and assuring operational continuity. Corporate social responsibility means understanding that company results improve to the extent to which companies are able to build relationships based on trust with their stakeholders. Therefore, it is essential not only to identify and assimilate the environmental, social and economic effects of the company’s activity, but also to analyze the impression held regarding these effects by company stakeholders so that, through the integration of these expectations into company strategy, any decision made takes into account the interests of stakeholders. This represents the transition from an individualistic company to one that takes into consideration the environment to which it is committed, to which it must respond, and with which it generates a long-term relationship of trust.

Photo taken by Juan Botella Cuesta, from Befesa, for the 1st Edition of the Abengoa Sustainability Photography Contest
CSR, understood, therefore, as the integration into company strategy of stakeholder expectations, observance of the law and consistency with international standards of conduct, is one of the underpinnings of Abengoa culture.
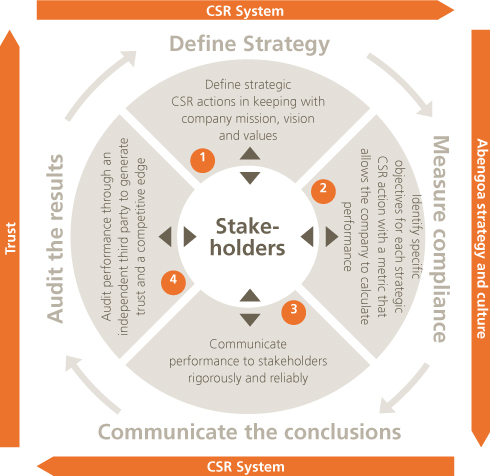
The concept of Corporate Responsibility framework therefore has:
- A legal dimension: strict observance of prevailing legislation in each and every one of the company’s actions;
- An economic dimension: generation of sustained value;
- A human dimension: protection of human rights;
- A social dimension: support of the development of the communities in which Abengoa operates;
- An environmental dimension: protection of the environment.
Each and every one of the activities undertaken by the company is carried out in accordance with the corporate model of sustainable development, a model that attempts to strike a balance with maximum benefits for everyone, while complying with applicable legislation with the utmost integrity and transparency. Thus, Corporate Social Responsibility is part of Abengoa’s business strategy and practice. Corporate social responsibility is one of the cornerstones of Abengoa’s present and future strategy. Each and every one of the activities undertaken by the company is carried out in accordance with the corporate model of sustainable development, a model that attempts to strike a balance with maximum benefits for everyone, while complying with applicable legislation with the utmost integrity and transparency. Thus, Corporate Social Responsibility is part of Abengoa’s business strategy and practice. Corporate Social Responsibility is one of the cornerstones of Abengoa’s present and future strategy.
For Abengoa, Corporate Social Responsibility must be perfectly aligned with company strategy and form part of it. Therefore, Corporate Social Responsibility strategy must be developed systematically and in a way that is consistent with the company’s mission, enabling it to be fully integrated into the core of the company’s decision-making process, into global strategy and into management processes and business activities.
Adopting a strategic approach to promoting CSR has numerous benefits: improvements in anticipating and managing risk, more appropriate management of reputation, attracting and retaining talent, greater competitiveness and market positioning, enhanced operational efficiency and cost reduction, improved relations along the supplier chain, a better relationship with the community, access to more sources of capital, and improved relations with regulatory bodies, among others.
Executive Corporate Social Responsibility Plan
The company has devised an Executive Plan for Corporate Social Responsibility to map out strategic actions for the three years following implementation. This plan defines global short, medium and long-term actions that entail all company areas, deploying this strategy by business units, with specific actions in CSR strategy, being adapted to the social reality of the different communities in which Abengoa conducts its business.
Fundamentally, this executive plan encompasses strategic actions that enable Abengoa to develop its distinctive capabilities in a setting of innovation and sustainability, while anticipating new business challenges associated with sustainability. The executive plan sets specific objectives for the strategic CSR actions, thereby enabling Abengoa to measure company performance by defining monitoring indicators.

Performance Disclosure and the Reporting System
In 2009, Abengoa completed implementation of its reinforced reporting system, which will be an effective means of providing the Abengoa management team with reliable consolidated annual information for the entire group concerning the relevant quantitative indicators in the area of Corporate Social Responsibility. The team can then manage the data accordingly and include it in the CSR report. In order for the information to be reliable, there must be systematic consistency in the consolidated data, which must be traceable or reconstructible, accurate and thorough in identifying and considering the data sources. For this reason, the reporting system also features effective internal control mechanisms that aid in preventing, detecting and rectifying significant errors in the data reported. In 2009, a specific CSR auditing area was set up to carry out ongoing and regular internal controls to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of the Abengoa’s reporting system. In addition, the system will be further complemented in 2010 by the implementation of a computer application that will combine the company’s existing reporting tools, thus allowing instant access to data and enabling updated data in real time.
Environmental Sustainability Indicator System
In 2009, Abengoa also developed a system of Environmental Sustainability Indicators (ESI), which will help to improve the company’s business management by enabling the company to measure and compare the sustainability of its activities and establish future objectives for improvement. The system will be put in place in 2010 and will allow Abengoa to be recognized not only as a company working towards sustainable development, but also as a company whose processes are carried out in a sustainable manner.
Abengoa’s Engagements
In 2002, Abengoa signed the United Nations’ Global Compact, a global initiative intended to achieve voluntary commitment from the business community to social responsibility by implementing ten principles based on human rights, labor and environmental standards and anti-corruption efforts.

Corporate Social Responsibility is the commitment of the business community to act ethically and contribute to economic development, while respecting the environment, enhancing quality of life for employees and their families, as well as that of communities and society at large