 Abengoa
Abengoa
Annual Report 2012
- Legal and Economic-Financial Information
- Consolidated analytical report
- Risk management and internal control
During 2012, Abengoa continued to grow, carrying on activities in more than 70 countries. To deal with this growth in a safe and controlled manner, Abengoa has a common business management system that allows it to work on an efficient, coordinated and consistent basis.
Abengoa is aware of the importance of managing its risks in order to carry out appropriate strategic planning and attain the defined business objectives. To do this, it applies a philosophy formed by a set of shared beliefs and attitudes, which define how risk is considered, starting with the development and implementation of the strategy and ending with the day-to-day activities.
These elements constitute an integrated system that allows for proper risk management and controls at all levels of the organization.
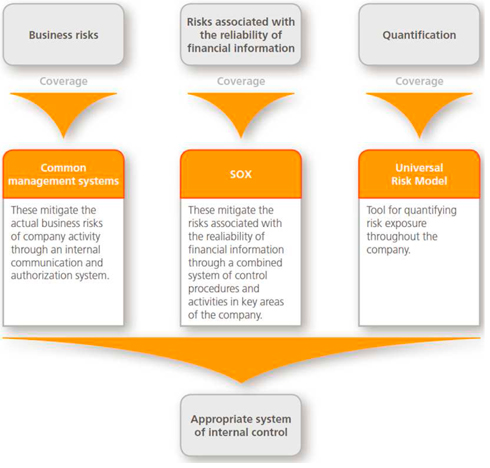
Business risks
Common management systems represent Abengoa's internal rules and all its business units and its methodology for assessing and controlling risks. They also represent a common culture for the various businesses of Abengoa and comprise 11 standards that define how management has each of the potential risks included in the risk model of Abengoa. Through these systems risks are identified and appropriate hedging and control mechanisms are defined.
Common management systems include specific procedures covering any action that may be a risk to the organization, both financial and non-financial. They are available to all employees on computer regardless of geographical location and job title.
Over recent years, the common management systems have evolved to adapt to the new situations and environments in which Abengoa operates, with the overriding aim of reinforcing risk identification, covering risks and establishing control activities.
Risks relating to the reliability of financial information
Abengoa began in 2004 an internal process of aligning its internal control structure over financial reporting with the requirements imposed by Section 404 of the SOX Act ("Sarbanes Oxley Act").
The purpose of SOX is to ensure transparency in the management, accuracy and reliability of the financial information published by companies listed on the U.S. market ("SEC registrants"). This law requires these companies to submit their internal control system to a formal audit by its financial auditor who, in addition, will provide an independent opinion on it. According to instructions of the "Securities and Exchange Commission" (SEC), this law is mandatory for companies and groups listed in the U.S. market.
Abengoa considers this legal requirement as an opportunity for improvement and far from satisfied with the conditions set out in the law, we have tried to develop the most of our internal control structures, control procedures and assessment procedures applied.
The initiative comes in response to the quick expansion of the group in recent years, and expectations of future growth, and to continue to provide investors with accurate, timely and complete finantial information.
During 2012 Abengoa has completed the implementation of SAP GRC Process Module Control. This tool provides a technology solution with the purpose of automating our internal control system and compliance monitoring, facilitating compliance and increasing security for the Company's operations.
The universal risk model
In 2011, Abengoa finished integrating its universal risk model, the company's chosen methodology for quantifying the risks that compose the risk management system. The goal is to obtain a comprehensive view of them, designing an efficient response system and aligned with business goals of the company.
Abengoa’s universal risk model is made up of four categories, 20 sub-categories and a total of 57 principal risks for the business. Each these risks has an associated series of indicators that allow its probability and impact to be measured and the degree of tolerance to the risk to be defined, thus allowing for subsequent risk assessment and monitoring.
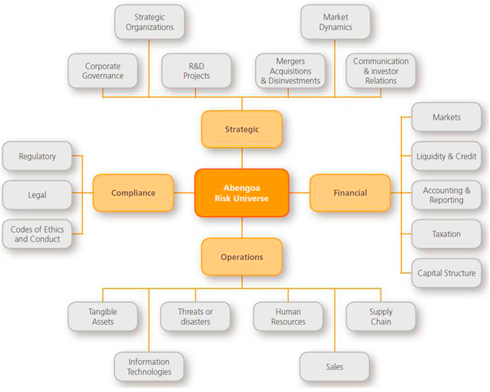
The risks identified in this model are evaluated considering two parameters:
- Likelihood of happening: Degree of frequency with which you can ensure that a particular cause will cause a negative impact event with Abengoa.
- Impact on Abengoa: Set of potential negative effects on Abengoa's strategic objectives.
Pursuant to the allocation probability and impact indicators for all the risks in the risk model Abengoa universal risks are qualified in 4 types (lower risk, tolerable risk, severe risk and critic risk). Each of these categories is treated with a risk management different strategy.
Abengoa has completed the implementation of Archer eGRC, technology solution that automates the process of identification, assessment, response, monitoring and reporting of risks that make up the universal risk model to keep all activities and sectors in which Abengoa operates.
During 2012, this application has been consolidated as a tool for calculation and reporting of identified risks. Since its introduction, Abengoa has been working on the application synchronization with other tools within the group with the aim of increasing process automation.
© 2012 Abengoa. All rights reserved
