 Abengoa
Abengoa
Annual Report 2012
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Strategy for a sustainable future
- Strategy aimed at responsible performance
Abengoa’s strategy, which seeks to position the company as an international benchmark in the development of groundbreaking technological solutions for sustainability, is rooted in systems and tools that measure its performance while also allowing us to improve the company’s decision-making processes and responsible management.
In its responsible management model, Abengoa prioritizes the need to integrate stakeholder expectations into its strategy. Employees, customers, suppliers, shareholders, the communities in which the company operates and the society are the cornerstone of CSR, and dialog with these stakeholders is key to generating relationships based on trust.

Master Plan: sustainability within the company’s strategy
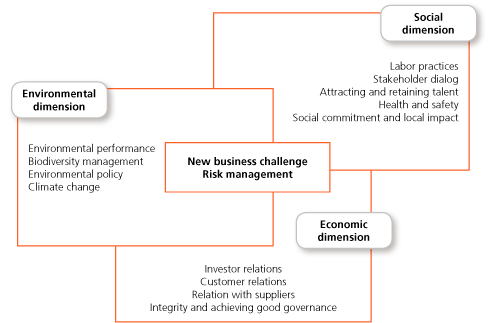
In 2008, Abengoa devised a CSR Master Plan, establishing the strategic lines for the entire company to follow in aspects relating to CSR in all its dimensions: economic, social and environmental.
The Master Plan has been gradually entrenched throughout the different levels of the company and in the different regions in which Abengoa operates. Regular committees with the CRS and business-unit managers have been set up to track and monitor the plan.
A Committee of skilled will also be set up in 2013, comprising the heads of the most important CSR divisions. This Comittee will analyse and update the strategic lines of the current plan to bring them in line with the prevailing business, environmental and social situation. Also it will address address and respond to stakeholder expectations. In going about this task, the committee will rely on the recommendations of the Independent Panel of Experts in Sustainable Development (IPESD) and all the materiality analyses conducted over the last two years1.
The various subject areas of the Master Plan are structured and managed through McKinsey’s three growth horizons, enabling the company to handle three scenarios simultaneously based on the extent to which each of the areas has been developed and integrated into the company.
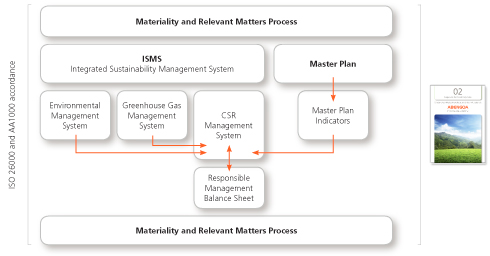
Integrated Sustainability Management System
In order to manage responsible performance, Abengoa has set up an Integrated Sustainability Management System (ISMS) to gather information relating to the social, environmental and economic impacts of its activity.
The ISMS comprises three component systems: the system CSR Management System, the Greenhouse Gas Inventory and the Environmental Management System.
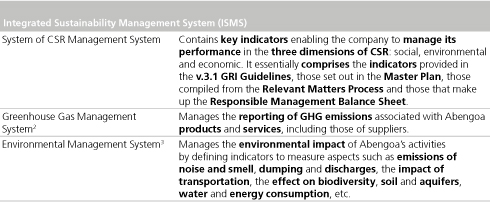
The ISMS pursues the following main objectives:
- Obtaining reliable consolidated data by capturing and verifying the information gathered by the three systems.
- Improving decision-making and rendering the company’s management more efficient by providing exhaustive data obtained in real time.
- Tracking changes in the indicators and designing improvement plans to lower the negative impacts of company business on society, the environment and the economy
- Reporting and disclosing information reliably and transparently to the company’s stakeholders.
In relation to the latter objective, the ISMS has internal and external audit and control mechanisms in place. External auditing is conducted by two independent entities. On the one hand, AENOR, in accordance with the ISO 14064-1:2006 Standard, reviews the information on Greenhouse Gases from activities involving direct and indirect energy consumption and other direct Abengoa emissions. KPMG, on the other hand, reviews the qualitative and quantitative information with which the ISMS addresses the main and supplementary GRI indicators included in the CSRR. Both of these independent review processes are performed with a reasonable level of assurance4.
In 2012, Abengoa continued to make improvements to the ISMS and continued to integrate it with the company’s other systems to ensure reliable data. The system currently has over 3,000 users across all the territories in which Abengoa operates.
Note 1: For further information on the GHG Management System, please see the chapter on the Environment.
Note 2: For further information on the Environmental Management System, please see the chapter on the Environment.
Note 3: For further information please see the chapter titled “About this report”.
Note 4: For further information please see the chapter titled “About this report”.

Photograph awarded the runner-up prize at the IV edition of the sustainable development photography competition, taken by Paola Alpresa Gutiérrez.

© 2012 Abengoa. All rights reserved
